Personalized Long-COVID Treatment: A Case Study – Part Two
Last week on our blog, one of our patients shared his experience with Long COVID and how we have been helping him on his journey to recovery (see “Recovering from Long COVID: A Case Study.”) His symptoms started after three bouts of Covid-19 in as many years, and even though he was a strong and healthy 63-year-old, the disease had taken a toll on his resiliency — his body’s ability to bounce back after a serious illness.

When we first met him, Doug was physically weak and exhausted and cognitively impaired (both thinking and memory). He had already consulted two other doctors who told him that conventional medicine had no effective treatment protocol for Long COVID and that his symptoms were likely to last for six to 24 months. They recommended that he enroll in a Long-COVID program available through the University of Florida.
We offered a better solution — a personalized plan of care to restore his health, fitness, and resiliency.
In this post, I share additional details about the personalized treatment protocol we prescribed for Doug at PROVOKE Health. But first, we offer a few words of caution.
Not a One-Size-Fits-All Approach
Here at PROVOKE Health, we practice functional medicine and integrative healthcare — a systems-based, whole-body approach that focuses on restoring health instead of merely eliminating illness or suppressing symptoms. That’s why functional medicine is effective in treating health conditions that conventional medicine cannot resolve.
Unfortunately, it is also why what works for one patient may not work for another. Every patient is unique and has special medical needs based on their age, genetics, medical history, family health history, lifestyle, health and fitness objectives, as well as other variants. We do not have a “long-COVID treatment protocol” that we prescribe to all our patients who report symptoms of long COVID. What we offer is a personalized plan of care, which evolves over time as the patient’s health improves.
In this post, I share the personalized plan of care we prescribed for Doug. We caution against using this as a standardized long-COVID treatment protocol or as a way to self-medicate. Prior to treating any patient, we conduct a thorough evaluation, which may include ordering lab tests to determine specifically what the patient needs. Taking too much or too little of a medication or supplement, poor quality products, or the wrong combination of medications and supplements, can do more harm than good. We recommend that you work closely with a certified functional and integrative medical practice in order to obtain personalized, medically supervised treatment.
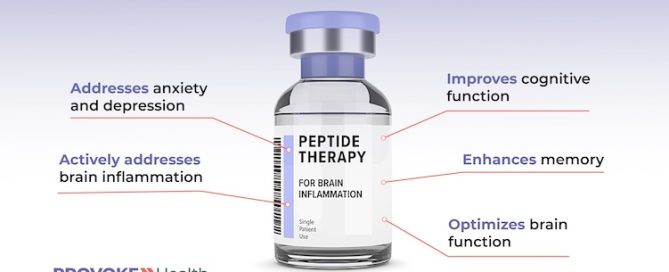
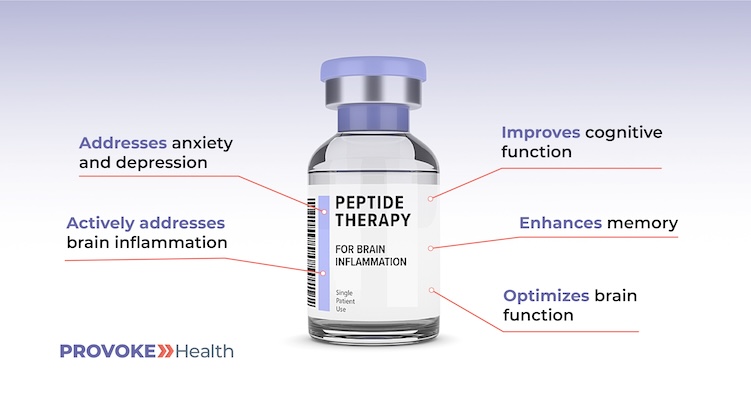
Doug’s Long-COVID Plan of Care
For Doug, we developed the following personalized plan of care. Below, Doug’s doses have been omitted intentionally because they are patient-specific and because recommended doses of some medications and supplements change as the patient’s health improves over time. Medical interventions, including prescription medications and intravenous treatments are provided by our medical team using trusted compound pharmacies: Continue reading…